Radiant barrier plywood enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer in buildings. Reflecting radiant heat away helps maintain cooler indoor temperatures during hot seasons, ultimately leading to lower energy costs. This innovative material combines the benefits of traditional plywood with advanced insulation technology, making it a popular choice for homeowners and builders alike.
As more people seek sustainable building solutions, understanding the advantages of radiant barrier plywood becomes essential. It contributes to energy savings, improves comfort, and potentially increases property value. Those interested in construction trends will find that integrating this product can significantly impact performance and efficiency.
Exploring radiant barrier plywood's features and installation processes reveals its practicality for various applications. Whether in new builds or renovation projects, this material offers an effective strategy for achieving energy savings and improving the living environment.
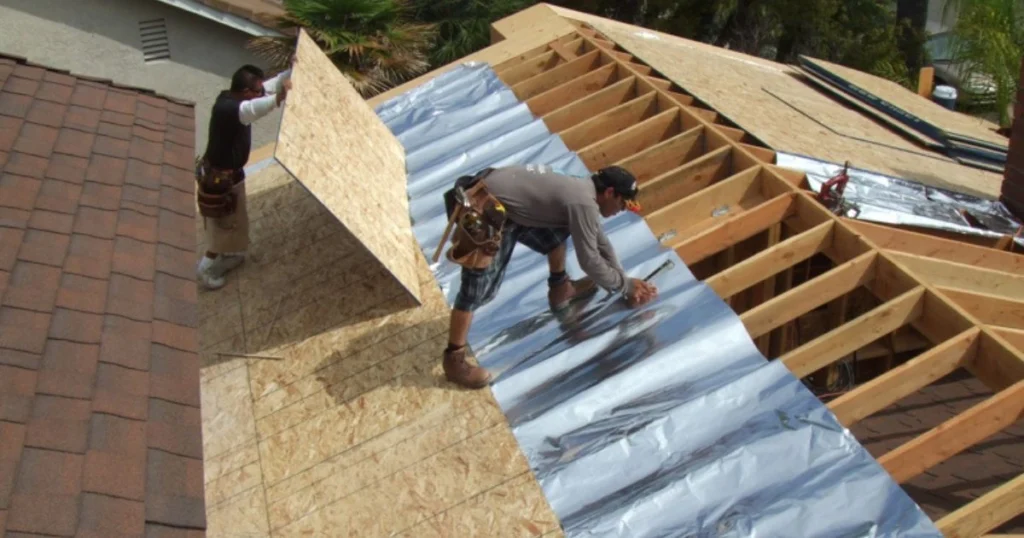

Radiant barriers are essential in managing heat flow in buildings. They function primarily through the reflective properties of their materials, influencing energy efficiency and comfort levels.
Radiant barriers have a relatively modern history, emerging in the mid-20th century as energy efficiency took center stage. Their development was influenced by advancements in materials technology aimed at minimizing energy loss. Initially used in commercial buildings, radiant barriers gained popularity in residential settings during the energy crises of the 1970s.
This demand prompted manufacturers to innovate, creating products like radiant barrier plywood and radiant barrier oriented strand board (OSB), which integrated insulation materials to enhance thermal performance.
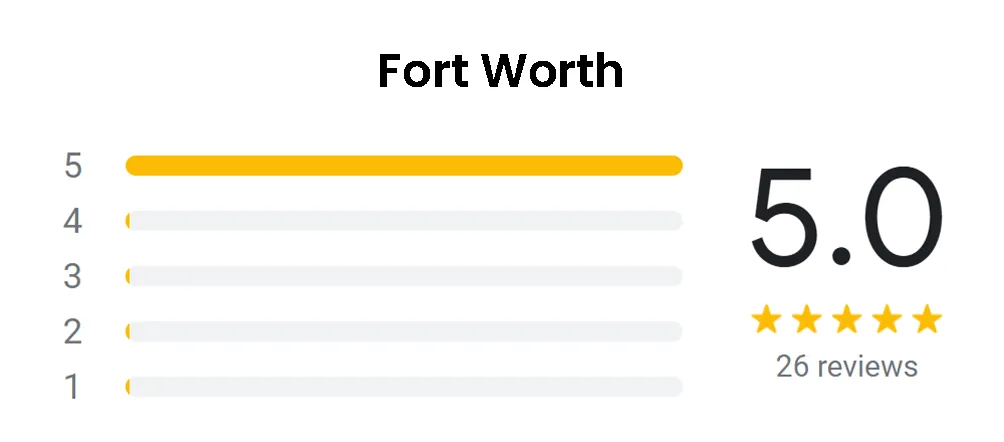
The fundamental principle behind radiant barriers is heat transfer via radiation. In simple terms, heat naturally moves from warmer areas to cooler ones. Radiant barriers reflect radiant heat away from living spaces, maintaining more stable indoor temperatures.
They work best in hot climates where cooling costs are a concern. The effectiveness of a radiant barrier is measured by its reflectivity and emissivity, the latter representing a material's ability to emit absorbed heat. High reflectivity and low emissivity allow these barriers to prevent heat gain effectively.
Various types of radiant barriers are available, tailored for different applications. The most common are radiant barrier plywood and radiant barrier OSB.
Both types can be installed during construction or retrofitted into existing structures, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort.
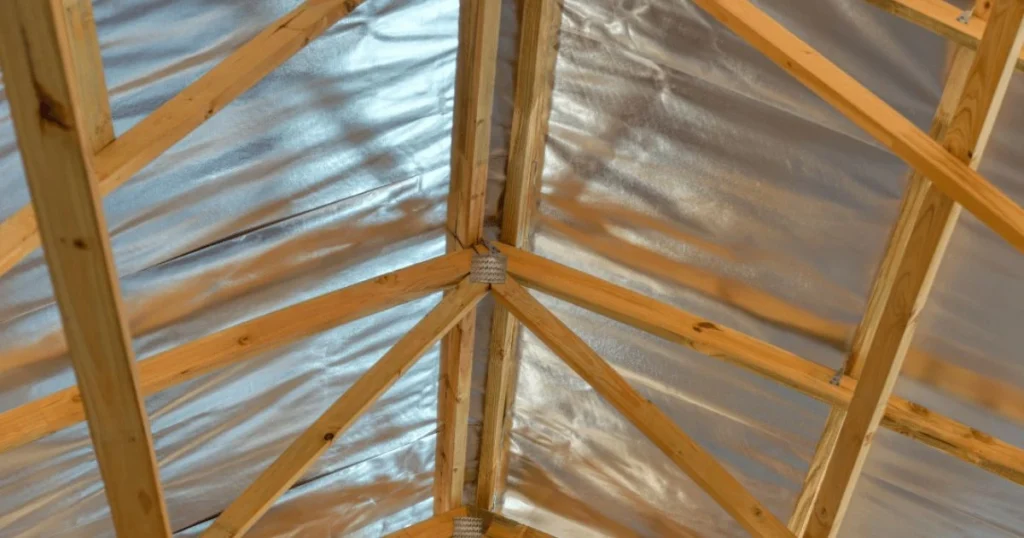

Radiant barrier plywood combines traditional plywood materials with reflective properties that enhance energy efficiency. Its design reduces heat transfer, making it suitable for various construction applications.
Radiant barrier plywood features a layer of reflective material laminated to one side of standard plywood. This reflective surface can be made from aluminum foil or other reflective materials.
Key characteristics include:
This plywood type is particularly effective in attics and roof structures, where heat accumulation can be significant.
Radiant barrier plywood is used in residential and commercial buildings to improve energy efficiency.
Typical applications include:
Builders and homeowners often choose this material for its dual function as standard plywood and energy-efficient radiant barrier. It meets building insulation codes while offering structural support, making it a versatile choice in modern construction projects.
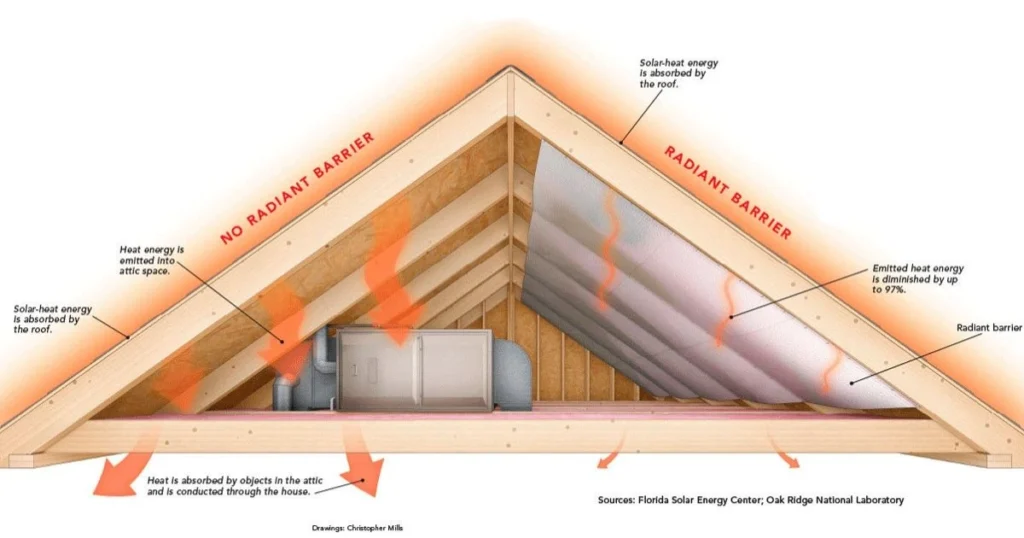
Radiant barrier OSB incorporates a reflective layer to decrease solar heat gain, making it an effective choice for energy-efficient building projects. The following sections cover key features and advantages that set this product apart from traditional OSB.
Radiant barrier OSB is designed with a layer of reflective foil applied to standard oriented strand board (OSB). This configuration enhances the material's thermal performance. A typical thickness is 7/16 inches, providing strength and stability suitable for roofing and walls.
The reflective layer minimizes radiant heat transfer. This feature is especially beneficial in hot climates, as it helps maintain cooler indoor temperatures. The durable surface also resists moisture, reducing the potential for mold growth. Additionally, radiant barrier OSB can be installed similarly to conventional OSB, allowing easy integration into existing building practices.
Radiant barrier OSB offers several advantages over traditional OSB. It improves energy efficiency by reflecting heat away from living spaces, which can result in lower energy costs, particularly in heated and cooled buildings.
Installation time can also be reduced, as radiant barrier OSB comes ready to use without additional heat-reflective coatings. Homeowners and builders may appreciate its role in contributing to a more comfortable indoor environment. It can still perform effectively in colder seasons, helping retain indoor warmth. Its versatility makes it suitable for various applications, enhancing its appeal within the construction industry.

Proper installation of radiant barrier plywood plays a crucial role in maximizing energy efficiency. Adhering to best practices ensures the radiant barrier effectively reduces heat transfer.
Before installation, gather the necessary tools and materials. Essential items include a utility knife, measuring tape, safety goggles, and protective gloves. Accurately measuring the roof area is vital to determining how much radiant barrier roof sheathing is needed.
Inspection of the underlying structure is crucial. Ensure that the roof deck is clean, dry, and free from debris or damage. Address any repairs prior to installation to ensure a secure fit. Familiarizing yourself with local building codes regarding radiant barriers can prevent future issues.
Installation begins with positioning the radiant barrier plywood against the roof joists. To enhance thermal performance, align the panels without gaps. To ensure stability, fasteners should be placed at intervals of 12 inches along the edges and every 24 inches in the field.
It's essential to maintain consistent airflow around the radiant barrier. Keep gaps at the eaves and ridges to allow for ventilation space. In humid climates, adding insulation on the interior side can further optimize performance. Follow the manufacturer’s specific guidelines for cutting and fitting the panels for a seamless installation.
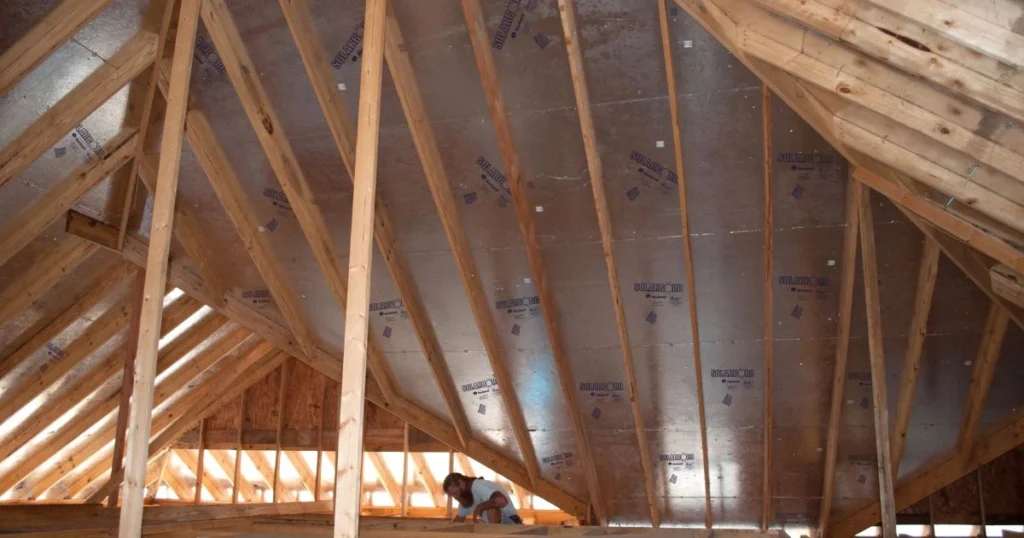

Radiant barrier plywood offers several benefits that enhance energy efficiency, lower costs, and promote environmental sustainability. These aspects make it an attractive option for homeowners and builders looking to improve structural performance.
Radiant barrier sheathing significantly improves energy efficiency in buildings. This material reflects radiant heat away from living spaces, reducing the heat that enters homes during hot weather.
In colder climates, it helps maintain warmth by reflecting heat back into the living area. This dual action of reflecting heat in summer and winter can lead to a more stable indoor climate.
Radiant barrier plywood lowers energy consumption by reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems, which can be measured in decreased utility bills over time.
Utilizing radiant barrier sheathing can lead to substantial cost savings for homeowners. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional plywood, the long-term benefits often justify the cost.
Lower energy bills are a significant factor, with studies showing reductions of up to 30% in cooling costs.
Additionally, enhanced energy efficiency can prolong the lifespan of HVAC systems, reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Homeowners may also find that such improvements can increase property value.
Radiant barrier plywood contributes positively to environmental sustainability. Promoting energy efficiency decreases the carbon footprint associated with heating and cooling.
With less energy consumption, there is a reduced demand for power generation, which can lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, many radiant barrier products are made from sustainable materials, aligning with eco-friendly building practices. Investing in this technology supports individual savings and broader environmental goals.
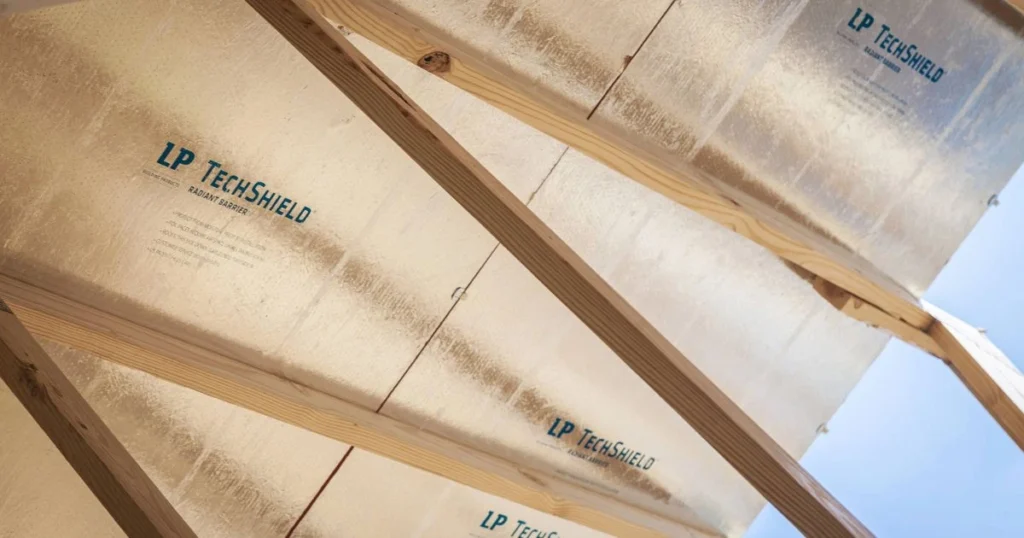

Several factors affect the efficacy and suitability of radiant barrier plywood, including climate conditions and inherent drawbacks.
The effectiveness of radiant barrier plywood largely depends on the climate. It can significantly reduce heat gain in hot climates, enhancing energy efficiency. In contrast, its benefits may not be as pronounced in cooler climates. If not properly integrated with insulation strategies, it might even lead to potential heating issues during winter months.
Geographic location also plays a role. The plywood’s moisture resistance and durability are vital in areas with high humidity or flooding risks. Homeowners must assess these factors to determine the ideal application of radiant barrier plywood in their specific environment.
While radiant barrier plywood offers advantages, it has limitations. Installation can be more complex and expensive compared to traditional materials. Furthermore, incorrect installation may result in reduced performance.
When used inappropriately, there is also a potential for condensation buildup, which can lead to mold growth. This is particularly crucial in climates with significant temperature fluctuations.
Finally, radiant barrier plywood may not provide adequate insulation if it is the sole material used. Combining it with other insulation methods is often necessary for optimal performance.
When considering radiant barrier plywood for construction or renovation, various complementary products and alternatives enhance energy efficiency and building performance. These options can optimize insulation and temperature regulation in spaces, often working in conjunction with radiant barriers.
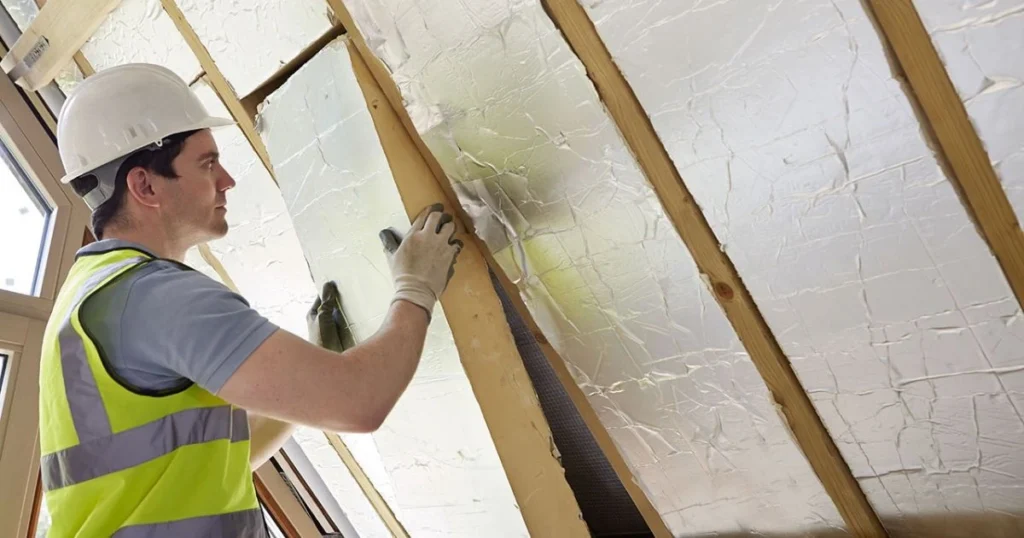
Various insulation materials can enhance the benefits of radiant barrier plywood.
Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice due to its cost-effectiveness and resistance to moisture. It can be installed in walls, attics, and floors to effectively reduce heat transfer.
Foam board insulation offers higher R-values (thermal resistance) and can be an excellent alternative. Products like rigid foam boards can be used alongside radiant barrier OSB to provide a solid thermal break.
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper materials, providing an eco-friendly option. This material can fill gaps in walls and attics, minimizing air leaks and maximizing energy efficiency.
Hybrid systems integrate multiple components to improve thermal performance and energy savings. Combining radiant barrier plywood with a spray foam insulation system creates a powerful barrier against heat transfer. The foam adds an air-sealing quality that complements the radiant barrier's reflective properties.
Another effective hybrid approach is radiant barrier OSB with a traditional insulation system. This combination gives optimal insulation while reflecting radiant heat away from living spaces.
Lastly, considering reflective roof coatings can further enhance a structure's heat management. These coatings work effectively with radiant barriers, providing additional energy savings, particularly in hot climates.
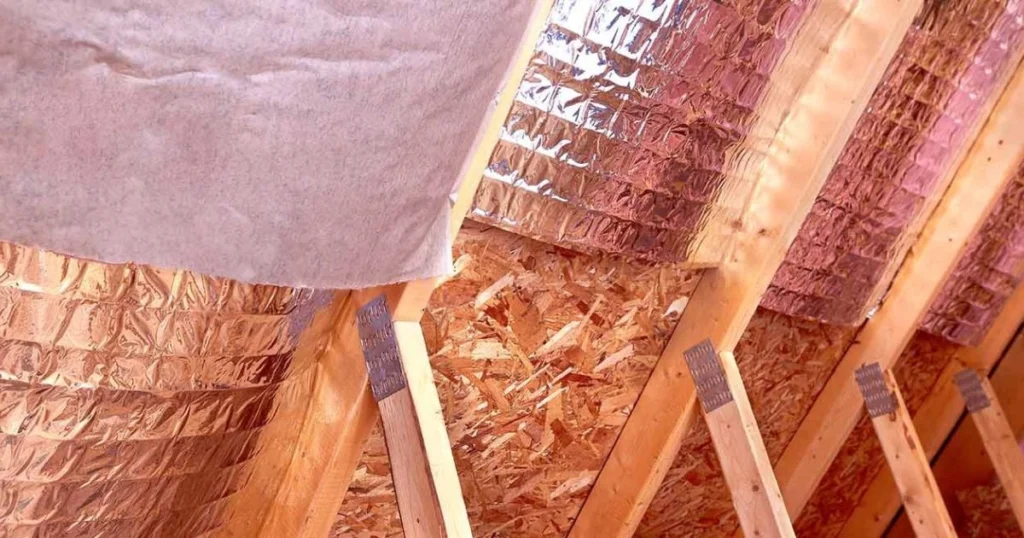

Maintaining radiant barrier plywood is crucial for maximizing its longevity and effectiveness. Proper care can extend the life of radiant barrier roof sheathing and maintain its thermal performance.
Radiant barrier plywood is designed for durability, but environmental factors can impact its lifespan. Proper sealing is vital to prevent water damage when exposed to moisture. Manufacturers often treat these barriers with coatings that enhance resistance to rot and mold.
Regular inspections are important. Checking for signs of wear or damage ensures that the plywood continues to perform efficiently. Any deterioration in the radiant barrier's surface can diminish its effectiveness, so early detection is key.
High-quality radiant barrier products typically resist UV degradation, but prolonged exposure can still impact performance. Maintaining an attic ventilation system can help mitigate heat buildup, preserving the integrity of the radiant barrier sheathing.
Caring for radiant barrier plywood involves a few essential steps. It is important to keep the surface clean and free from debris. A gentle wash with water and mild detergent can remove dirt without damaging the barrier's reflective surface.
If damage occurs, repairs can be straightforward. Small holes or cracks can be sealed with appropriate roofing sealants recommended by the manufacturer. Replacing the damaged section of plywood may be necessary for larger areas of concern.
Proper ventilation in the installation area can reduce the risk of condensation, impacting repair needs. Regular assessments of the radiant barrier roof sheathing ensure it remains an effective component of the building's thermal envelope.
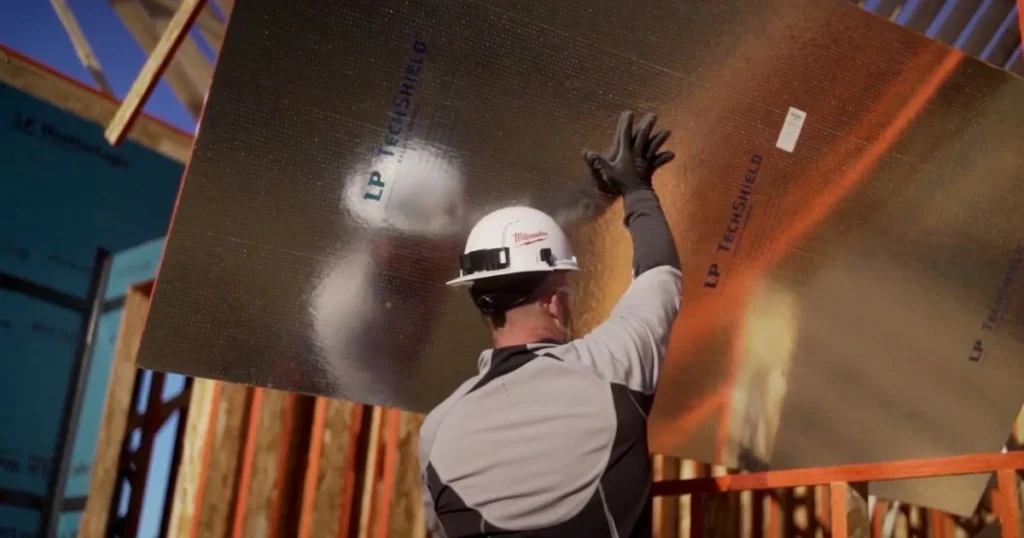

Radiant barrier plywood and oriented strand board (OSB) must meet industry standards and quality assurance measures. These guidelines ensure that products are safe, effective, and environmentally friendly.
Radiant barrier plywood typically complies with standards set by organizations such as the American Plywood Association (APA) and the International Code Council (ICC). These standards focus on structural integrity, moisture resistance, and environmental impact.
Various certifications, such as Engineered Wood Products (EWP) and Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI), indicate compliance with safety requirements. Furthermore, radiant barrier materials often undergo testing for thermal performance and reflectivity according to ASTM International standards. Manufacturers' adherence to these guidelines ensures that radiant barrier systems perform as intended in residential and commercial applications.
Quality assurance processes for radiant barrier plywood involve monitoring production and conducting regular inspections. Manufacturers often implement third-party testing to validate thermal efficiency and moisture resistance claims.
Products may also be subjected to rigorous quality control measures, including durability tests and performance evaluations. A quality assurance program helps maintain consistency and reliability in radiant barrier materials. This focus on quality can lead to better insulation performance and longer service life in home construction and retrofitting.
For those dealing with wildlife or pest issues, contacting Critter Stop is an option. This professional, humane wildlife removal company offers free inspections and holds a fantastic reputation for excellent service. To resolve pest problems effectively, call Critter Stop at (214) 234-2616.
This section addresses common inquiries about radiant barrier plywood, its benefits, and its performance compared to traditional materials. Each question will clarify how it contributes to energy efficiency and heat management in construction.
Radiant barrier plywood reduces radiant heat transfer, keeping buildings cooler in hot climates. This can decrease air conditioning costs and improve comfort levels in living spaces. Additionally, it can enhance the overall efficiency of an HVAC system.
Radiant barrier OSB targets radiant heat, while traditional insulation materials focus mainly on conductive and convective heat transfer. This unique quality allows radiant barrier OSB to work with other insulations, potentially enhancing thermal performance.
The R-value for radiant barrier plywood typically ranges from R-3 to R-5, depending on the thickness and specific product. This value indicates its resistance to heat flow, making it effective in reducing energy consumption.
Radiant barrier sheathing employs reflective technology to bounce radiant heat away from the building. This reflective surface minimizes heat absorption, especially in attics and roofs, creating a more energy-efficient environment.
Yes, OSB with a radiant barrier is an excellent choice for new constructions. It provides enhanced energy efficiency and can contribute to meeting building codes that aim to reduce energy consumption.
The 7/16-inch thickness offers a balance between structural integrity and thermal performance. It adequately reduces heat transfer while maintaining ease of installation and cost-effectiveness.
5/8-inch radiant barrier plywood is advisable when additional strength is necessary, such as in areas with high snow loads or strong winds. This thickness provides extra durability while still contributing to energy efficiency.
Installing 1/2-inch radiant barrier plywood in attics improves insulation and minimizes heat buildup. It is suitable for residential projects where space and weight considerations are critical, offering effective thermal management without adding excessive weight.
Visit our Critter Library and learn more about our furry friends