Rats and mice are some of the most common household critters that people confuse. We regularly get asked, “are a rat and mouse the same?” While they are relatively similarly in appearance, they are still quite different. Since customers often ask us what is the difference between a mouse and rat, we created this article to answer their question! At Critter Stop, we regularly help customers with rats, mice, squirrels, raccoons, and much more!

A primary difference between rats and mice is their size. Rats are generally larger than mice, with some species growing up to 18 inches long. Mice, on the other hand, are much smaller, usually measuring around 2-4 inches in length. Another key difference is their behavior. Rats are known to be more aggressive and territorial than mice, often fighting with each other for food and shelter. Mice, on the other hand, are more social and tend to live in larger groups.
Despite these differences, rats and mice share many similarities. They both have sharp teeth and long tails, and are infamous for spreading diseases. They are also both excellent climbers and quite crafty when trying to find their way into homes, exploiting small cracks and openings. Understanding the differences between rats, mice, and other critters can help homeowners take the appropriate measures to keep them out of their homes and prevent infestations.
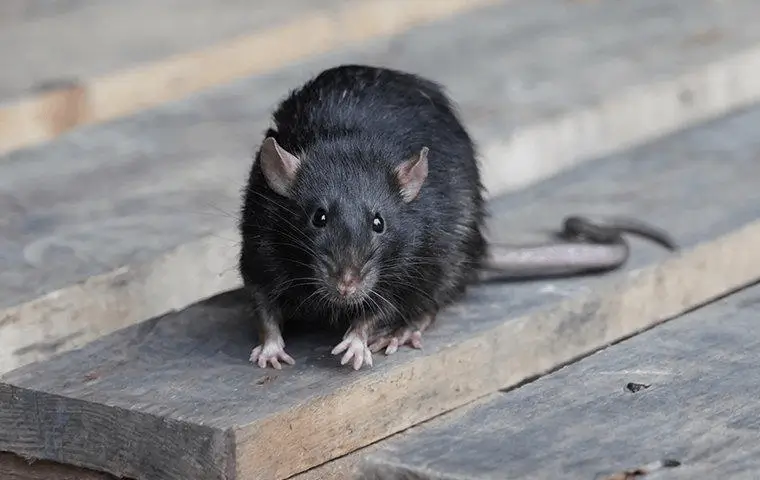
Rats belong to genus Rattus and are "medium-sized" relative to other rodents. They have long, pointed snouts, and large, curved ears. They have long, scaly, hairless tails, and their fur can be brown, black, or gray. They have sharp teeth, which they use to gnaw through hard surfaces like wood and metal. They are also known for their strong sense of smell and excellent hearing.
Rats are also social creatures, usually living "colonies." Regularly joining seafaring humans, rats are remarkably found across the glove. They are known for their adaptability to different environments. Rats are omnivores, eating both plants and animals. This helps them adapt and thrive in a variety of habitats, including urban areas, forests, wetlands, plains, and deserts.
Mice belong to the family Muridae and are on the smaller size relative to other rodents. They have round, furry bodies, large ears, and long, thin tails. Their fur can be brown, black, or gray, and they have short snouts. Mice are agile and fast, helping them avoid predators. Mice are also social creatures that live in colonies. Similarly, they are also found all over the world and are omnivores. They too can be found in various habitats.
In conclusion, while rats and mice share some similarities, they are different animals with unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these differences can help people better identify and manage rodent infestations.
Mice and rats are similar in many ways, but one of the most obvious differences is their size. Mice are smaller than rats, typically measuring between 2.5 and 4 inches in length, with a tail that is about the same length as their body. Rats, on the other hand, are larger, measuring between 9 and 11 inches in length, with a tail that is longer than their body. A roof rat (also called black rat or ship rat), can weigh ~2.5-8 oz, while a brown rat, also known as a Norway rat, can weigh approximately double, at ~5-17oz. If you have bought the traps before, you probably already knew this difference in rat vs mouse size since rat traps are several times larger than mouse traps.
Similarly, rat droppings are much larger than mouse droppings. Rat droppings and mouse droppings are the most common indication of rodent activity, so this is often easier than comparing the size of the animals themselves. Rat droppings, which are usually a little larger than a grain of rice, are ~3x the size of mice droppings, which are smaller than the typical grain of rice.
Both rat and mouse droppings are black - if you find brown rat droppings, it is more indicative of diet and age than the animal itself. The darker the rodent droppings, the fresher they are.
While house mice and field mice droppings are so small and similar that they are hard to discern, the roof rat and Norway rat produce a distinct dropping shape. Key differences in rat droppings help us identify the species, and thus the best way to deal with the animal. Both are oval, but a roof rat has a pointy end on one side of the feces (kind of like a roof, which is an easy way to remember it) while a Norway rat will produce much more rounded ends on both sides.
Another physical difference between mice and rats is their fur and color. Mice have short, soft fur that is usually brown or gray, while rats have coarser fur that can be brown, black, or gray, depending on the type of rat itself. While there are several different names, the U.S. is dominated by the following two rats:
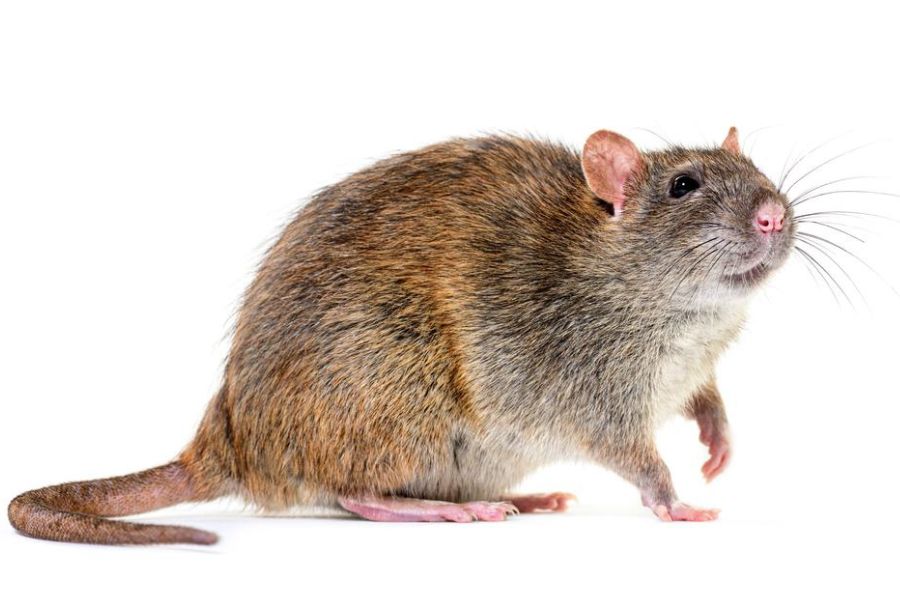

Instead of using scientific names like Rattus Norvegicus, or saying "ship rat" when the vast majority of readers will not be experiencing rats on ships, we will refer to them as "roof rats" and "Norway rats." In regards to fur color, roof rats typically have greyish-black fur while Norway rats usually have brownish-grey fur. This is obviously to be expected, but a key distinction is that roof rats have pale underbellies.
"Field mice" have brown or gray fur with white underbellies, while "house mice" are just one single solid color throughout their body - no underbelly.
Lastly, both the roof rat and Norway rat will have a scaly tail, while both a field mouse and a house mouse will have a furry tail.
Mice and rats also have different facial features and body structures. Mice have small, round ears and a pointed snout, while rats have larger, more prominent ears and a blunt snout. Rats also have a more robust body structure, with a thicker neck and broader shoulders than mice.
In summary, while mice and rats share many similarities, including their rodent classification and similar behavior patterns, there are also a couple noticeable physical differences between the two species. Mice are smaller, have shorter fur, and distinct facial features, while rats are larger, have coarser fur, and a more robust body structure.
When it comes to behavior, rats and mice differ in several ways. This section will cover some of the primary differences in behavior.
One of the biggest differences between rats and mice is their nesting habits. Mice tend to build their nests in hidden and isolated locations, such as inside walls, attics, and basements. On the other hand, rats are more likely to build their nests in open spaces, such as in burrows or under debris. Foraging Behavior of Rats vs Mice
Another significant difference between rats and mice is their foraging behavior. Mice are known to be more curious and exploratory when it comes to finding food. They will search for food in various locations and are more likely to try new foods. This is one reason you will see mice chew on just about anything. However, rats are more cautious and tend to stick to familiar food sources. They will also hoard food for later consumption.
Rats and mice also differ in their social behavior. Mice are generally more social and prefer to live in groups. Mice will play with each other, groom one another, and even sleep together. Rats, on the other hand, are more territorial and aggressive towards other rats. They will fight to establish dominance and may even kill other rats if they feel threatened.
In summary, rats and mice have significant behavior differences. Mice tend to build their nests in hidden locations, are more exploratory when it comes to finding food, and are more social. Rats, on the other hand, build their nests in open spaces, are more cautious when it comes to food, and are more territorial and aggressive towards other rats.
Rats and mice have different lifespans. Generally, rats live longer than mice. The average lifespan of a rat is around 2-3 years, while the average lifespan of a mouse is around 1-2 years. However, there are some species of mice that can live up to 4 years. The lifespan of both rats and mice can be affected by various factors such as genetics, diet, and living conditions.
Rats and mice also have different breeding habits and reproduction rates. Rats have a longer gestation period than mice. The gestation period for rats is around 21-23 days, while for mice, it is around 19-21 days. Rats also have fewer litters per year than mice. On average, rats have 4-6 litters per year, while an adult mouse can have up to 10 litters per year.
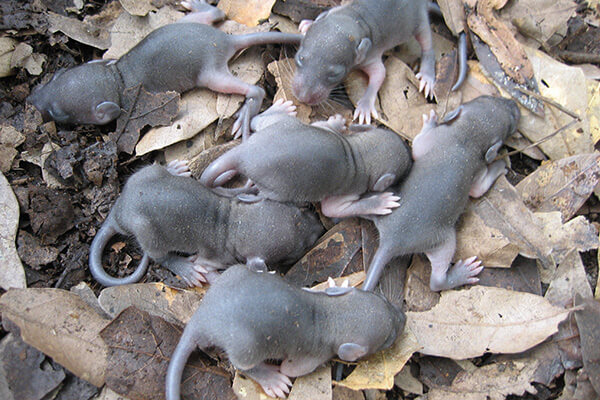

In terms of litter size, rats tend to have fewer offspring per litter than mice. Rats usually have 6-12 offspring per litter, while mice can have up to 14 babies per litter. Rats also have a more prolonged reproductive period than mice. Rats can reproduce for up to 2 years, while mice can only reproduce for up to 1 year.
Overall, while rats and mice may look similar, they have significant differences in their lifespan and reproduction rates. These differences can impact their behavior, physiology, and interactions with humans.
Rats are adaptable to various environments and can survive in different habitats. They prefer to live in areas with abundant food sources, water, and shelter. Rats can be found in fields, forests, and urban areas. Roof rats tend to live in nests in trees or in warm, safe attics, while Norway rats thrive in sewers, crawl spaces, garbage dumps, and abandoned buildings. They create burrows and nests to protect themselves from predators and harsh weather conditions.
Mice prefer to live in areas with vegetation, such as fields, meadows, and forests. They also like to live in areas with abundant food sources and water. Mice are smaller than rats and can easily squeeze through small openings and cracks. While they both often live in colonies, when directly compared, mice are more likely to live in small groups or alone and create nests in hidden places, such as inside walls, attics, and basements..
Both rats and mice can adapt to urban environments. However, rats are more adaptable to urban environments than mice. Rats can survive in sewers, subways, and other areas with a lot of human activity. They can also feed on garbage and other waste products. Mice, on the other hand, prefer to live in areas with vegetation and are less adaptable to urban environments.
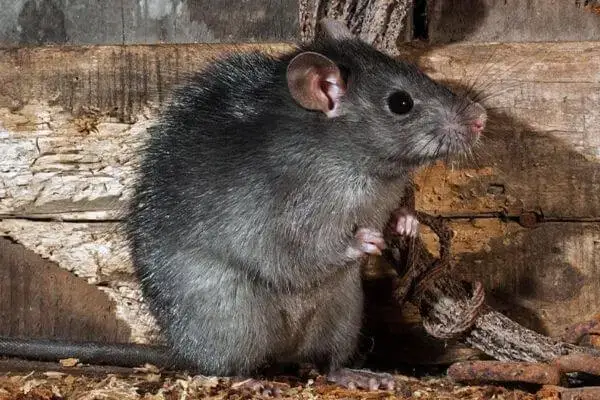

In conclusion, while both rats and mice have similarities in their habitats, they have distinct differences in their preferred environments. Rats are more adaptable to urban environments, while mice prefer areas with vegetation.
Rats are known to be carriers of various diseases that can be transmitted to humans. They can spread diseases through their droppings, urine, and saliva. Some of the diseases transmitted by rats include leptospirosis, salmonella, and hantavirus. These diseases can cause severe illness or even death in humans.
Rats are also known to carry fleas, which can transmit diseases to humans and animals. The bubonic plague, also known as the Black Death, killed millions of people. It was spread by fleas carried by rats.
Mice are also carriers of diseases that can be transmitted to humans. They can spread diseases through their droppings, urine, and saliva. Some of the diseases transmitted by mice include hantavirus, salmonella, and Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). These diseases can cause severe illness or even death in humans.
Mice are also known to carry ticks, which can transmit diseases to humans and animals. Lyme disease, which is transmitted by ticks carried by mice, can cause long-term health problems if not treated early.
Rats and mice can cause significant damage to properties. Rats are known to gnaw through electrical wires, which can cause fires. They can also damage insulation, pipes, and other structures in buildings. Rats can contaminate food and water sources, which can cause health problems for both humans and animals.

Mice can also cause damage to properties. They are known to gnaw through electrical wires, which can cause fires. Mice can also damage insulation, pipes, and other structures in buildings. Rats can contaminate food and water sources, causing health problems for humans and animals.
In conclusion, while rats and mice may appear similar, there are significant differences in their impact and interactions with humans. Both rats and mice can transmit diseases and cause damage to properties. It is essential to take measures to prevent infestations and to seek professional help if an infestation occurs.
When it comes to controlling rats, there are several methods that are commonly used. These include:
Similarly, there are several methods that are commonly used to control mice. These include:
Correctly identifying whether you are dealing with rats or mice is crucial for effective control. This is because the two species have different behavior patterns and preferences for food and shelter. For example, rats are more likely to burrow and prefer moist environments, while mice are more likely to nest in walls and prefer drier environments.
In addition, different control methods may be more effective for rats versus mice. For example, snap traps are usually more effective for rats, while glue traps are more effective for mice. If you can correctly identify whether you are dealing with mice or rats, you can choose the most appropriate control methods and increase your chances of success.
Overall, effective management and control of rats and mice requires a combination of different methods, including traps, poison baits, exclusion, and habitat modification. Correctly identifying the species you are dealing with is also crucial for effective control.
In summary, mice and rats are different in several ways. Mice are smaller in size, have pointy snouts, and have larger ears and eyes in proportion to their body size. Rats, on the other hand, are larger, have blunt snouts, and smaller ears and eyes in proportion to their body size. Additionally, rats have thicker tails and larger feet than mice.
Another key difference between the two is their behavior. Mice are generally more curious and exploratory, while rats are more cautious and tend to avoid new objects in their environment. Mice are also more likely to nest indoors, while rats prefer to nest outdoors.
In Critter Stop, we understand that the differences between mice and rats are crucial in pest control and management. It helps determine the most effective methods for preventing and controlling infestations. For example, since mice are more curious, they are more easily caught in traps baited with food. In contrast, rats are more cautious and may require different types of traps or bait.
Additionally, since mice are more likely to nest indoors, it is important to seal up any openings in the walls or foundation of a building to prevent them from entering. Rats, on the other hand, may require more extensive measures, such as removing outdoor food sources and debris that may attract them to the area.
Overall, understanding the differences between mice and rats is crucial for effective wildlife removal. It helps determine the best approach for preventing and controlling infestations, and ensures that the most appropriate methods are used for each spec.
If you're having a problem with any of these rodents, give us a call at (214) 234-2616 and our team will be ready to pick up the phone and hear the situation. We will go to your house to do a free inspection and prepare everything to solve your rodent problem!
Visit our Critter Library and learn more about our furry friends